Water Treatment for the Energy Industry
Water treatment for the energy industry
Electricity generation requires huge volumes of water, used at almost every stage of the process — from boiler feed systems to cooling condensers and bearings, as well as pollution scrubbers. Clean water is critical not only at the intake stage, but also at discharge. Environmental legislation continues to evolve, tightening restrictions and shifting demand toward zero liquid discharge (ZLD) solutions. As a result, innovation in water treatment for the power sector is steadily increasing.
According to trend analyses, global water demand is expected to grow by 55% due to population growth, while electricity demand will increase by 45 trillion kWh, or approximately 44% more than in 2018. This creates a dilemma: power plants depend heavily on water to generate clean energy. The solution lies in advanced technologies combined with engineering expertise, enabling smarter, cleaner ways to conserve, treat, and reuse water to meet the needs of an increasingly connected, electrified world.
Electricity generation is one of the largest industrial consumers of water, with most of it used for on-site cooling. In addition to cooling water, boilers and flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems or wet scrubbing systems also contribute significantly to overall water consumption. Due to the large water volumes required, power plants are typically located near natural water sources, such as rivers, from which water can be withdrawn for operational use.
Untreated or insufficiently treated water can lead to erosion and damage to steam-generating equipment. Inadequately treated wastewater discharges may violate environmental regulations. Thanks to advanced technologies, new solutions are transforming how water is treated, recycled, and reused in the production of clean and renewable energy.
Water treatment systems used at power plants
Several types of water treatment systems are applied in the energy sector, including:
• Pretreatment: removes suspended solids, colloidal particles, organic matter, and minerals such as iron and manganese.
• Boiler feed water treatment: minimizes impurity levels that could damage or impair boiler operation.
• Condensate polishing: reduces suspended metals, particulates, and other contaminants that may cause corrosion and increase downtime.
• Cooling tower blowdown treatment: reduces corrosion and treats discharged cooling water.
• Flue gas desulfurization (FGD): removes sulfur oxides, heavy metals, and gypsum from wastewater generated during power production.
• Recycling and reuse: treated effluents are recycled and reused to ensure a continuous supply of clean water.
Water preparation in the energy sector
Water treatment systems are a critical component of any energy facility, as water quality directly affects the service life and performance of the entire system. Scale formation and corrosion processes are direct consequences of inadequate or low-quality water treatment.
Water sources for combined heat and power plants (CHP) and thermal power stations may include municipal water supplies (for facilities located within cities) or independent water sources, such as wells, boreholes, or surface water intakes. In the case of municipal water, achieving optimal water quality parameters often requires softening (single- or two-stage) and deaeration (chemical or physical oxygen removal).
In addition, it is often necessary to adjust pH levels and dose chemical reagents that inhibit corrosion in pipeline systems. When using water from wells or boreholes, treatment systems must include pretreatment stages, typically involving the dosing of strong oxidizing agents.
Key aspects of water treatment for thermal power plants
Today, membrane filtration systems based on nanofiltration and reverse osmosis technologies are widely used in water treatment for thermal power plants. These solutions significantly reduce operating costs and minimize environmental impact.
A key feature of water treatment for cooling systems at power plants is the need to prevent fouling of heat exchange surfaces. This is achieved through continuous or periodic dosing of chemical reagents into the treated water. The type, dosage, and dosing interval are determined based on the operational requirements of a specific system.
A relatively new but rapidly developing area in the energy sector is water treatment for gas turbine combined heat and power plants. The importance of producing water of the required quality continues to grow, making advanced water treatment solutions increasingly essential for modern energy facilities.
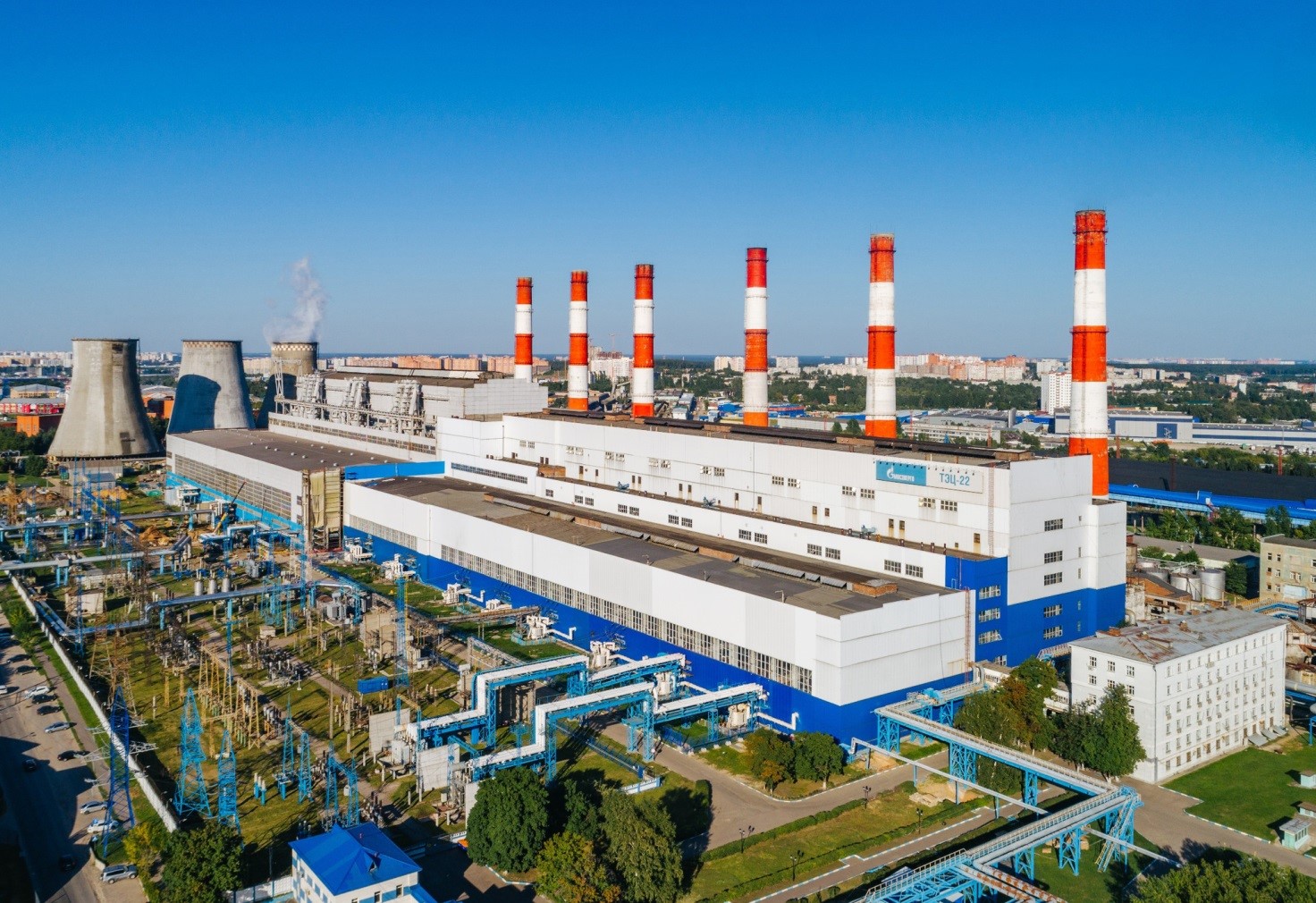

CHP plants generate thermal and electrical energy, which is supplied to residential buildings and industrial facilities. The operating principle of such plants is based on heating water by burning certain types of fuel. When heated, water is converted into steam, which drives turbines that generate electricity. After that, hot water is supplied to district heating systems of residential buildings and industrial enterprises.
The main problem in the operation of CHP equipment is solid deposits formed during water heating:
Scale
Scale is deposited on the internal mechanical surfaces of boilers, heat exchangers, and pipelines, reducing operating efficiency, shortening equipment service life, and increasing energy consumption for heat and electricity generation. In many cases, this leads to breakdowns or complete failure of expensive equipment that can no longer be restored.
Corrosion
When untreated water is used at CHP plants, it contains large amounts of substances that promote corrosion formation:
· oxygen;
· acids;
· alkalis;
· free carbon dioxide;
· chlorides.
All of these are active stimulators of corrosion processes. Corrosion reduces operating efficiency and shortens the service life of thermal power equipment. This leads to decreased production of electrical and thermal energy and often becomes the cause of accidents at CHP plants.
Bacteria
Bacteria that enter thermal power equipment together with untreated water or during maintenance work also contribute to corrosion. Pitting corrosion forms on metal surfaces, rust clogs boilers, heat exchangers, pipelines, and heating mains. This results in reduced equipment efficiency, increased energy consumption, and may lead to emergency situations and shutdowns of CHP operations.
Ways to solve these problems through water treatment for CHP plants

The only effective way to solve all the above-mentioned problems at CHP plants is the installation of water treatment systems and filters for high-quality water purification. For this purpose, several key water treatment methods are used:
- Preliminary mechanical treatment
As a rule, to remove large mechanical impurities, rust, and sand, disc, mesh, or reagent-free (column-type) filters, as well as ultrafiltration units for deep mechanical purification, are installed at the initial stage of the system.
- Iron removal
Iron removal allows both oxidized and dissolved iron to be eliminated from water. For this purpose, filters with special filter media are installed, which remove iron from the water supplied to hot-water boilers.
- Sorption filters
For sorption treatment of water at CHP plants, filters with special media are used, most commonly activated carbon. These filters remove chlorine-containing compounds, heavy metals, and eliminate taste, color, and odor from the source water.
- Water softening
Water softening involves the removal of hardness salts — calcium and magnesium compounds that precipitate when water is heated and form scale on metal surfaces of equipment. To remove hardness salts, ion-exchange resin filters are used. In these filters, hardness salts are converted into sodium ions, after which clean and safe water is supplied to thermal equipment.
- Reverse osmosis water treatment
Reverse osmosis technology is the most effective method for treating water with a high concentration of dissolved salts. Under high pressure, source water is forced through fine-pore membranes that allow only water molecules to pass through while retaining up to 99.9% of organic substances, contaminants, and dissolved salts.
How to choose an industrial reverse osmosis system?

There are several recommendations that help select a high-performance and efficient industrial reverse osmosis system for water treatment at CHP plants. Key selection criteria:
- Dimensions. A reverse osmosis system with the same capacity but a more compact design allows saving valuable floor space.
- Inlet pressure supplied from the water supply system or another water source. This parameter must be no less than 3 bar. If the pressure is lower, it is necessary to choose a system equipped with a booster pump to generate the pressure required for efficient reverse osmosis operation.
- Expected water consumption. It is important to calculate anticipated water demand in advance to ensure uninterrupted and efficient equipment operation. This makes it possible to determine the optimal capacity of the industrial reverse osmosis system.
Advantages of reverse osmosis technology
Industrial reverse osmosis systems are capable of effectively removing 97–99.9% of impurities from water supplied from open sources, wells, or municipal water networks. Such systems also offer a number of additional advantages:
- Wide range of models with different functionality and capacities. This allows selection of an optimal system in terms of size, configuration, and performance for any technological process.
- High-quality water purification without the use of harmful or expensive chemical reagents or heating, which significantly reduces energy and financial costs.
- Maximum purification efficiency for removing various chemical substances and organic contaminants, including bacteria and viruses.
- Capability to desalinate large volumes of seawater for use at CHP plants.
- Reliability, maintainability, and affordable service costs, limited mainly to replacement of filter elements.
- Compact design of industrial reverse osmosis units, which helps save space and significantly reduces installation costs as well as the overall cost of organizing a water treatment system at CHP plants.
- Low operating costs per 1 m³ of treated water compared to other water treatment technologies.
Ready-made and custom water treatment solutions for CHP plants from ZIKO

The company ZIKO is one of the recognized leaders of the Ukrainian water treatment and purification market. We offer cost-effective and efficient standard or customized solutions for water treatment at industrial enterprises, CHP plants, and in the housing and utilities sector.
By contacting us, you will receive a comprehensive range of high-quality services:
· We carry out water sampling and analysis to determine the presence and concentration of contaminants in our own laboratory.
· If required, our specialists will help formulate the technical assignment.
· Our engineers will design a water treatment solution tailored to the technological requirements of any enterprise.
· Our specialists will deliver the required equipment to the customer’s site, install, configure, and commission a turnkey reverse osmosis system.
· We will take full responsibility for repairs, maintenance, and replacement of filter elements throughout the entire service life of the industrial reverse osmosis system.
A quality warranty is provided for all equipment, both standard and custom-designed industrial water treatment solutions developed by our specialists, as well as for installation and maintenance services.
Would you like to implement efficient and cost-effective water treatment at a CHP plant, but are unsure about system configuration or how to correctly calculate equipment capacity?
Write to us or call us. Our engineers will promptly perform all necessary calculations, select the most efficient equipment, and help you organize a reliable and high-quality water treatment system for your enterprise, fully aligned with your specific needs.
- Published in Рішення, Системи водопідготовки – рішення
Water Treatment at Distilleries
The company ZIKO develops and implements solutions for effective water treatment at distilleries using modern industrial water filtration systems. Our equipment enables efficient removal of contaminants, reduction of water hardness, and lowering of total mineralization of the incoming water.
During the treatment process, organic compounds are removed, while color and turbidity are eliminated. Industrial water treatment in alcohol production significantly improves the quality of the final product and has a positive impact on the subsequent quality of spirits and alcoholic beverages. Transparency, taste, and aroma are enhanced, and the shelf life of beverages is extended without loss of organoleptic properties.
Water treatment in alcohol production is a guarantee of excellent product quality.

Alcohol is a raw material for the production of alcoholic beverages. The quality of the final product — its appearance and organoleptic properties — directly depends on its characteristics. Therefore, water treatment at a distillery is a critical stage in the further production of spirits and liqueurs, during which the following objectives are achieved:
Reduction of water hardness
High-quality water treatment in alcohol production makes it possible to reduce hardness — that is, to lower the concentration of magnesium and calcium cations in the source water to optimal values of 0.2–1.0 mg-eq/L. This prevents the formation of sediment in the final product after alcohol is blended with water.
After proper water treatment, no sediment forms in bottles containing fruit or berry tinctures and liqueurs. At low concentrations, magnesium and calcium ions do not react with tannins and pectins present in fruits and berries, and therefore insoluble compounds are not formed.
Reduction of total mineralization
If water treatment is not carried out during alcohol production, mineral elements present in water significantly impair the appearance and reduce the organoleptic properties of the final product:
- sodium chloride gives beverages a salty taste;
- high concentrations of iron and copper cause a metallic aftertaste;
- sodium and magnesium sulfates impart bitterness;
- the presence of calcium sulfate makes alcoholic beverages harsh and astringent.
Elimination of turbidity and color
Industrial water treatment at distilleries allows the concentration of humic substances — which give liquids a yellow-brown coloration — to be reduced almost to zero. As a result, alcoholic products acquire a clear and attractive appearance.
During water treatment in alcohol production, suspended particles and colloidal elements are removed. This improves the visual quality of alcoholic beverages and eliminates opalescence — cloudiness that can occur during long-term storage.
Water analysis is a key stage of water treatment in alcohol production

For high-quality water treatment in alcohol production, specialists of ZIKO carry out a detailed water analysis based on 22 key parameters in their own laboratory. Based on the results of this analysis, as well as the customer’s requirements for the quality of the final water, the most effective water treatment solution is designed or selected. After that, the system is engineered, supplied, installed, and commissioned. ZIKO provides a quality warranty for all equipment and services.
High-quality water treatment at a distillery is impossible without a detailed analysis of the source water. As a result of laboratory tests performed in our own laboratory, ZIKO specialists determine the presence and concentration of:
- calcium and magnesium ions, which affect water hardness — the key raw material for alcohol and spirit production;
- other mineral elements that negatively affect the taste and aroma of beverages;
- iron and other metals;
- ammonium, nitrites, nitrates, and hydrogen sulfide;
- humic substances, which cause water color and turbidity;
- other contaminants that influence the quality of the final product.
Based on the analysis results, the most efficient and productive water treatment equipment for alcohol production is selected. As a result, the customer receives exceptionally clean water — an ideal raw material for producing high-quality alcoholic beverages.
Water treatment at distilleries using industrial flow-through iron removal and water softening systemsи проточними системами знезалізнення і пом’якшення

Water Treatment at Alcohol (Ethanol) Production Facilities
The company ZIKO offers high-performance комплекс water treatment systems for iron removal and softening using time-proven filter media such as Ecomix, Dowex, Birm, and Filter-AG, which effectively remove:
• calcium and magnesium (water hardness);
• ammonium / ammonia;
• manganese;
• iron;
• hydrogen sulfide and other contaminants.
These systems are characterized by a relatively low cost, high capacity, and efficient operation.
Their main drawback is the use of a saline solution for system regeneration, which must subsequently be discharged into the sewer system. Continuous salt consumption significantly increases the cost of one liter of treated water, which directly affects the production cost of the final product.
Water Treatment at Alcohol Production Using Reverse Osmosis

Reverse Osmosis Technology
Reverse osmosis technology involves the use of filters with special membranes. These membranes purify the feed water at the molecular level by allowing water molecules to pass through while retaining dissolved fine impurities.
Advantages of water treatment for alcohol production using reverse osmosis:
• removal of arsenic, heavy metals, fertilizers, Na, Ca, Cl, Fe ions, pesticides, and other harmful contaminants — the feed water is purified to an almost ideal condition;
• compact system dimensions and the possibility of vertical membrane installation;
• high reliability and ease of maintenance;
• minimal energy consumption, which allows for significant savings on energy costs;
• environmental benefits, as no saline solution is required for regeneration and there is no discharge of brine into the sewage system;
• low operating costs compared to conventional water treatment systems (the system fully pays for itself within a few years due to the absence of salt consumption for regeneration).
Depending on production volumes and the requirements of technological processes, reverse osmosis systems are equipped with the required number of membrane elements. Their capacity can reach 50 m³/h or more.
An additional advantage of reverse osmosis systems is the ability to achieve extremely low levels of water contamination, ensuring a purity level sufficient for use in pharmaceutical applications, steam turbines, and, of course, for the production of high-quality alcohol, especially for export markets.
Would you like to receive more detailed information about water treatment methods for alcohol production and the equipment used?
Phone numbers and email addresses are available in the “Contacts” section. Write to us or call our managers — they will be happy to advise you on any questions and help you select the most efficient, high-performance, compact, and cost-effective water treatment equipment.
- Published in Рішення, Системи водопідготовки – рішення
Wastewater Treatment at Alcohol Distilleries
ZIKO Company — a Leader in the Water Treatment Market of Western Ukraine
For more than 30 years, ZIKO has been designing, developing, manufacturing, and installing equipment for wastewater treatment at alcohol distilleries, industrial enterprises, multi-apartment residential buildings, and private houses. Qualified personnel, in-house production, and a wide range of efficient water treatment systems and filtration units enable the company to handle even the most complex technical tasks.
At the initial stage of cooperation, company specialists conduct a detailed wastewater analysis to determine the presence and concentration of contaminants. Based on the results, equipment for wastewater treatment at alcohol production facilities is designed or selected and installed to remove the identified impurities. All water treatment services and implemented solutions are provided with a quality guarantee.
Purpose of Wastewater Treatment at an Alcohol Distillery
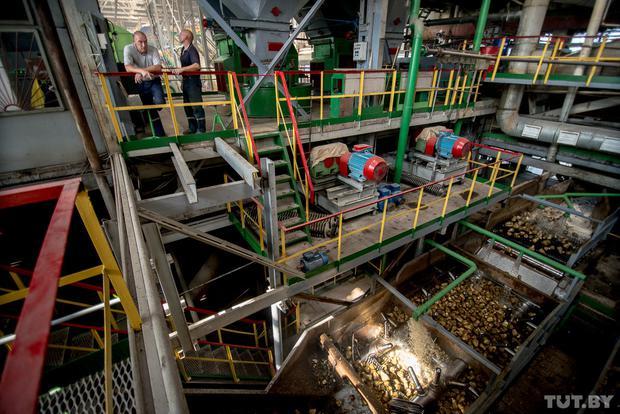

The primary raw materials for alcohol production include sugar beet, potatoes, and cereal crops. During their preparation and processing, large volumes of clean water are required for the following operations:
- Potatoes — washing of raw materials, rinsing of starch extracted from tubers, and cleaning of equipment used for filtration, dewatering, and evaporation of starch syrup.
- Cereal crops — washing and soaking during malting, cleaning of process equipment, malting screens, steam boilers, chemical treatment filters, and humidification of malting chambers.
- Sugar beet — washing of raw materials, cleaning of equipment after molasses processing, filter regeneration, and rinsing of equipment used in alcohol production.
After these technological processes, the wastewater contains large mechanical and organic impurities, biologically oxidizable substances, foreign microflora, and in some cases pathogenic microorganisms. All of these contaminants have a negative impact on the environment.
High-quality wastewater treatment in alcohol production ensures the effective removal of these pollutants. Treated water can be safely discharged into sewer systems, natural water bodies, soil, or reused in technological processes.
Methods and Equipment for Wastewater Treatment in Alcohol Production

Comprehensive Wastewater Treatment at an Alcohol Distillery involves the use of equipment implementing several water treatment methods:
- Mechanical treatment — removal of large solid particles from wastewater generated during alcohol production.
- Equalization (mixing of wastewater with varying concentrations) for subsequent feeding to the flotation unit.
- Flotation with coagulants and flocculants — conversion of colloidally stable and finely dispersed contaminants into larger agglomerates.
- Biological wastewater treatment in alcohol production processes.
Mechanical Wastewater Treatment at an Alcohol Distillery
Preliminary mechanical treatment of wastewater in alcohol production allows for the removal of suspended and solid particles. For this purpose, special screens and steel grates are used to retain large mechanical impurities and fine fibrous fractions. After this stage, the treated water is transferred to the next treatment step.
Equalization — the Next Stage of Wastewater Treatment in Alcohol Production
During wastewater treatment at alcohol production facilities, effluents are supplied to treatment units unevenly, due to:
- Hourly, shift-based, and daily fluctuations in wastewater volumes;
- Shock discharges following equipment washing;
- Emergency discharges caused by technological equipment failures.
Not only the volume but also the concentration of contaminants in the wastewater fluctuates. Therefore, to reduce the load on treatment equipment and ensure maximum treatment efficiency, equalization tanks are installed. These tanks stabilize both the contaminant concentration and the volume of wastewater.
Flotation — Wastewater Treatment in Alcohol Production Using Coagulants and Flocculants
Flotation is a method of wastewater treatment at alcohol distilleries carried out in special flotation units using air bubbles. Contaminants present in the wastewater adhere to the oxygen bubbles generated by the flotators and rise to the surface together with the air in an insoluble form.
To create optimal conditions and accelerate the flotation process, special reagents are applied:
- Mineral coagulants — aluminum, iron, and magnesium salts, lime;
- Organic and inorganic flocculants — alginates, yeast, starch, sodium silicate (activated silicic acid).
During flotation-based wastewater treatment in alcohol production, flotation sludge forms on the water surface as a contaminant-rich foam. This sludge is removed and directed to dewatering units.
Biological Wastewater Treatment in Alcohol Production

Biological Wastewater Treatment at an Alcohol Distillery can be carried out using two types of equipment:
- Aeration tanks — treatment units in which contaminated water is mixed with activated sludge by an air flow and saturated with oxygen. This ensures intensive biochemical oxidation of organic substances.
- Biofilters — tanks or artificial ponds equipped with drainage layers of filtering material (gravel, slag) at the bottom and covered with a biological film of aerobic bacteria. Contaminants are absorbed and oxidized by these microorganisms.
Biological wastewater treatment at alcohol distilleries provides the highest level of purification. The treated effluent is brought into compliance with regulatory requirements and can be safely discharged onto soil, into open water bodies, or reused in technological processes.
Sludge Disposal

The sludge generated during wastewater treatment in alcohol production can be handled in the following ways:
- Pumped out by vacuum trucks and disposed of in accordance with applicable regulations and legal requirements;
- Dewatered and transported to landfills designated for solid household waste storage;
- Used as fertilizer for agricultural crop cultivation.
Do you still have questions regarding wastewater treatment at alcohol distilleries, equipment characteristics, or water treatment methods? Please call or send an email using the contact details provided in the “Contacts” section. Our specialists will provide professional консультації, help you select the most optimal technology, and recommend efficient water treatment equipment for alcohol production facilities.
- Published in Промислові системи очищення стоків – рішення, Рішення
The engineering company ZIKO delivers ready-made solutions for removal of petroleum products from wastewater for enterprises in Lviv and other regions of Ukraine. The company also offers a wide range of filters, reverse osmosis systems, and other equipment for effective water treatment.
Company specialists:
- visit customer sites and perform a detailed water analysis;
- select equipment based on wastewater analysis results or design customized water treatment systems;
- install, commission, and start up systems for treatment of oil-contaminated wastewater, as well as provide maintenance and repair services.
A quality guarantee is provided for all equipment and the full scope of services.
Wastewater Treatment at Oil Refineries
High-quality removal of petroleum products from wastewater is a mandatory stage of refinery production cycles, as water is used as:
- a coolant for equipment, units, and finished products;
- a source of condensate and steam;
- a solvent for reagent mixing.
After use in these technological processes, wastewater may vary in contamination level and pollutant composition. It may contain:
- urea and ammonium ions;
- cyclic organic hydrocarbons and phenol;
- surfactants and paraffins;
- fatty acids, petroleum products, sulfates, and other contaminants.
Installation of oil separators or integrated systems for treatment of wastewater contaminated with petroleum products allows the effluent to be treated to a safe condition. After treatment, the water can be discharged into sewer systems, onto soil, into water bodies, or reused.
Technologies for Water Treatment from Petroleum Products
There are two main technologies for treatment of oil-contaminated wastewater:
- mechanical;
- physicochemical.
Mechanical Treatment of Wastewater from Petroleum Products

This wastewater treatment method used at oil refineries makes it possible to remove up to 65% of impurities from the effluent. Mechanical water treatment is based on sedimentation in oil separators. Wastewater is directed into tanks where, over a period of 6 to 24 hours, petroleum products are separated from the water. These tanks may be static or dynamic. In static units, the medium remains stationary, while in dynamic units it moves vertically or horizontally.
Physicochemical Treatment of Wastewater at Oil Refining Enterprises
This technology enables removal of both suspended solids and dissolved contaminants from wastewater. The most effective methods for treatment of water contaminated with petroleum products include:
- Flotation — removal of colloidal and dispersed contaminants using gas bubbles.
- Sorption — absorption of contaminants onto the surface of adsorbents (solid materials). Common sorbents include activated carbon, alumina gel, silica gel, and zeolites.
- Ion exchange — ion-exchange materials remove ions from the medium by replacing them with an equivalent amount of ions from the ion exchanger.
- Hyperfiltration — treatment of oil-contaminated wastewater using reverse osmosis systems. Wastewater is supplied under high pressure to semi-permeable membranes, where purification occurs at the molecular level.
- Neutralization — removal of acidic or alkaline components from the wastewater.
- Extraction — redistribution of contaminants between two mutually immiscible liquids.
- Evaporation — a method of wastewater treatment at oil refineries involving the passage of water vapor heated to 100 °C through the contaminated medium.
For more detailed information on methods for treatment of water contaminated with petroleum products, you may contact ZIKO specialists using the phone number provided in the “Contacts” section. Our managers will advise you on the selection of oil separators and provide comprehensive information on the technical characteristics and cost of water treatment equipment.
Equipment supply requests are also accepted via the company’s email address.
- Published in Побутові системи очищення стоків – рішення, Рішення
Mechanical Treatment of Industrial Wastewater
The engineering company ZIKO offers ready-made solutions for physicochemical, biological, and mechanical treatment of wastewater from industrial facilities and sewerage systems. A detailed analysis of the effluent is carried out, based on which treatment systems are designed, equipment is selected, and appropriate water treatment methods are defined.
Company specialists install, service, and repair mechanical wastewater treatment units and provide professional консультації on equipment selection. A quality guarantee is provided for the full range of services.
Mechanical Wastewater Treatment Methods
During mechanical wastewater treatment, solid and suspended particles are removed from the medium. This is a preliminary stage of wastewater preparation prior to discharge or reuse, during which the effluent is prepared for subsequent biological or physicochemical treatment.
The main mechanical methods for wastewater treatment at industrial enterprises and sewerage systems include:
- Screening. The primary stage of water treatment, during which wastewater passes through screens that retain fibers and insoluble impurities.
- Sedimentation — removal of suspended solids from wastewater. The method is based on gravitational forces, causing contaminants to settle at the bottom of sedimentation tanks.
- Filtration — separation of suspended solids by passing wastewater through fine-mesh screens or porous media such as anthracite, quartz sand, gravel, or similar materials.
- Centrifugation in hydrocyclones — separation of solid particles within a rotating flow of the medium.
After mechanical water treatment, sludge dewatering is performed. This process also consists of several stages:
- Preparatory stage. Preliminary dewatering of wastewater sludge is carried out using filter presses through conditioning by organic flocculation — aggregation of sludge using flocculants. This increases the sludge’s ability to release water.
- Main stage. The partially dewatered sludge layer obtained after the previous stage is covered with quicklime and converted into granules. During the reaction, the temperature of the solidified particle layer rises to +80 °C, promoting both dewatering and disinfection of the sludge.
- Final stage — complete dewatering of wastewater sludge by mechanical воздействие on the solidified particle layer using centrifugal force, vacuum, or pressure.
Facilities for Mechanical Wastewater Treatment
The main structural elements of facilities for mechanical wastewater treatment include:
- screens;
- grit chambers;
- sedimentation tanks.
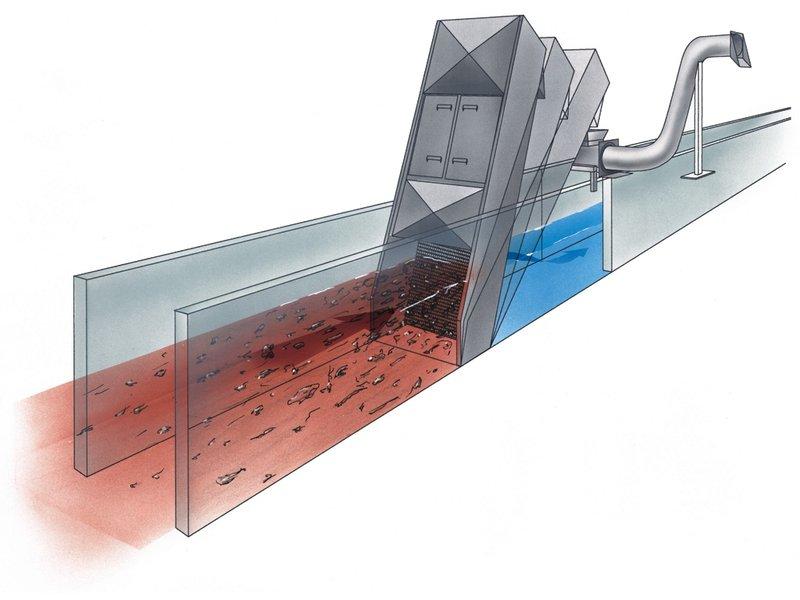
Using screens for wastewater treatment, large floating contaminants are removed from the flow. Screens may be movable or stationary and are installed at an angle of 65–75° to the horizontal. During operation, wastewater screens require regular cleaning to remove accumulated debris.
Grit chambers are designed to remove mineral contaminants from wastewater. The flow velocity through grit chambers must be adjusted so that only heavy mineral particles settle, while organic matter and finer particles are carried away by the water flow. Depending on the direction of wastewater movement, grit chambers are classified into three types:
- horizontal;
- vertical;
- slot-type — wastewater flows along the bottom of a special channel, where sand and impurities are separated.
Sedimentation tanks (grease traps) are reservoirs used for mechanical wastewater treatment in which contaminants are separated from a medium moving vertically or horizontally. Impurities may settle at the bottom of the tank or float to the water surface, depending on their physical properties.

Advantages of Mechanical Wastewater Treatment
Various mechanical wastewater treatment methods make it possible to remove the following from the effluent:
- large foreign objects;
- fats and oils floating on the wastewater surface;
- sand and other mineral particles.
A properly selected mechanical wastewater treatment method ensures effective preparation of the effluent for subsequent physical, chemical, or biological treatment.
The company offers cost-effective ready-made solutions for mechanical treatment of wastewater from industrial enterprises and sewerage systems. ZIKO specialists can visit the site, perform a detailed wastewater analysis, and recommend the most efficient water treatment equipment.
Detailed consultations regarding quality, technical characteristics, capacity, and cost of mechanical wastewater treatment equipment are available by phone using the number provided in the “Contacts” section. Requests for system design, development, equipment supply, and installation are also accepted via the company’s email address.
- Published in Побутові системи очищення стоків – рішення, Рішення
Methods of Wastewater Disinfection
The company ZIKO offers ready-made solutions for disinfection of wastewater from industrial enterprises and municipal sewerage systems. Treatment units and systems are designed with consideration of the specific operational conditions of plants, factories, workshops, and the composition of wastewater. During the design of wastewater disinfection systems, a detailed analysis of the effluent is carried out, based on which appropriate treatment methods are selected.
Purpose of Wastewater Disinfection
In addition to the removal of various contaminants, wastewater disinfection methods are applied to eliminate pathogenic microflora from the effluent. These microorganisms are the cause of a wide range of diseases, including:
- gastrointestinal diseases: salmonellosis, paratyphoid fever A and B, cholera, dysentery, and typhoid fever;
- viral diseases: hepatitis A and B, various types of poliomyelitis;
- infectious diseases: tuberculosis, adenoviral and enteroviral infections;
- parasitic and bacterial diseases: campylobacteriosis, amoebiasis, helminthiasis, brucellosis, and many others.
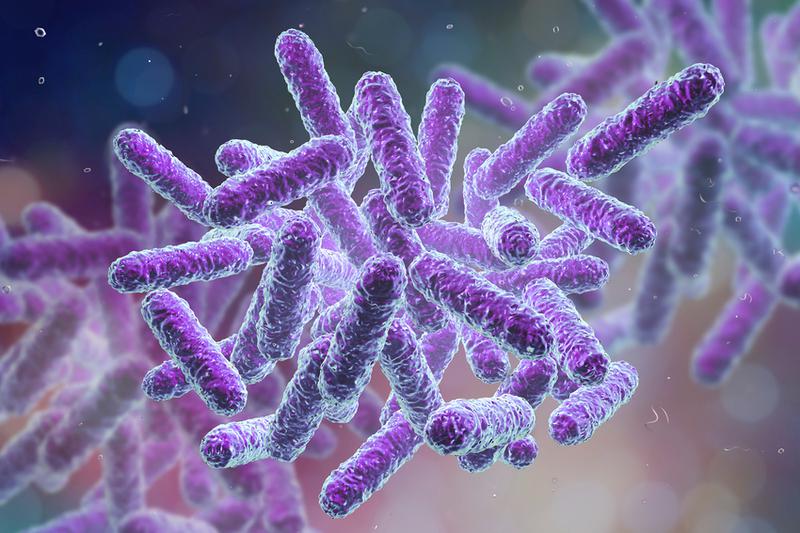
Various wastewater disinfection methods make it possible to eliminate the risk of negative impact of untreated effluent on the environment and human health.
Methods of Wastewater Disinfection
There are three main methods of wastewater disinfection:
- Chemical disinfection using hydrogen peroxide, ozone, chlorine, and other chemical compounds.
- Water treatment within natural or artificial biocenoses.
- Physical disinfection of wastewater using ultraviolet, electric, or electromagnetic radiation, or by exposure to elevated temperatures.
Chemical Wastewater Treatment
There are two approaches to chemical wastewater treatment:
- Neutralization — reduction or adjustment of pH to a range of 6.5–8.5 using various methods.
- Oxidation — a chemical reaction in which toxic substances present in the water are converted into less aggressive compounds, which are subsequently removed from the medium. During oxidation, chlorine and hydrogen peroxide are commonly used. Other oxidizing agents may also be applied, including calcium or sodium hypochlorite, pyrolusite, ozone, or oxygen.
Another widely used chemical method is ozonation of wastewater from industrial enterprises and sewerage systems. Ozone is introduced into the treated medium, where it decomposes organic compounds. Through this process, wastewater is purified from a range of contaminants, including:
- aromatic hydrocarbons;
- dyes;
- oxidized cyanides;
- petroleum products;
- phenol and surfactants.
During ozonation, wastewater is disinfected, decolorized, and unpleasant taste and odors are eliminated.
Physical Methods of Wastewater Disinfection
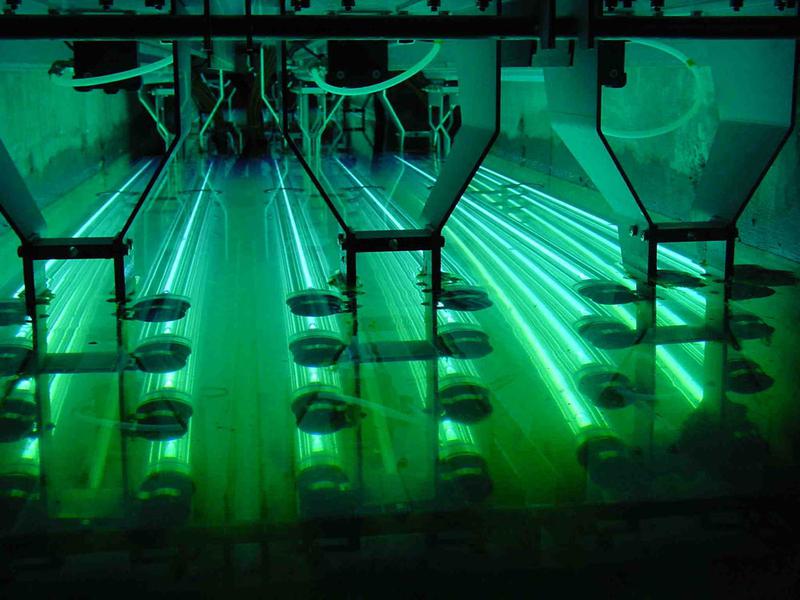

The most effective and widely used physical method of wastewater treatment is ultraviolet (UV) disinfection. This process is carried out by exposing the effluent to ultraviolet radiation with wavelengths ranging from 200 to 280 nm.
Ultraviolet wastewater disinfection offers several advantages:
- it is a reagent-free, environmentally safe, and ecologically clean water treatment method;
- ultraviolet radiation rapidly destroys microorganisms hazardous to human health;
- no harmful chemical reagents are used during UV disinfection, which significantly reduces overall treatment costs;
- high energy efficiency, resulting in lower power consumption;
- relatively low equipment cost, as well as simple operation and low maintenance expenses.
ZIKO specialists perform a thorough analysis of the effluent, after which appropriate solutions and disinfection methods are selected for industrial wastewater and municipal sewerage systems. The company provides a full range of services, including system design, development of integrated and standalone water treatment solutions, installation, and warranty and post-warranty maintenance.
For detailed information on service conditions, you may call the phone number provided in the “Contacts” section or send an email to the company. Our specialists will free of charge assist in selecting wastewater disinfection units optimized for price and technical characteristics and will provide information on equipment cost and installation timelines.
- Published in Промислові системи очищення стоків – рішення, Рішення
Types of Industrial Pumping Stations
ZIKO supplies a wide range of industrial sewage pumping stations with delivery across Ukraine for various application areas. All equipment complies with current quality standards. The company also supplies water filters, reverse osmosis systems, and provides services for design, engineering, configuration, and installation of water treatment and water preparation systems.
Purpose of Sewage Pumping Stations
The main function of sewage pumping stations (SPS) is to lift wastewater using pumps to a level required for gravity discharge into a water body, receiving reservoir, or sewer system. Such equipment is used for pumping:
- stormwater runoff;
- drainage water;
- industrial, domestic, and utility wastewater.
High-capacity sewage pumping stations are indispensable when wastewater must be transported across elevated terrain.
Types of Sewage Pumping Stations
Depending on installation and design features, industrial water pumps and sewage pumping stations are divided into three main types:
- Vertical stations. These units are most often manufactured from fiberglass and are equipped with two pumps operating alternately. Fiberglass SPS units are resistant to aggressive chemical environments. A vertical sewage pumping station may also be equipped with solid filtration devices, ventilation systems, and autonomous control systems.
- Horizontal stations. An industrial horizontal sewage pumping station operates on the same principle as a vertical unit but is equipped with submersible pumps and automatic liquid level monitoring systems.
- Stations with self-priming pumps. The housing of such a sewage pumping station has a cylindrical shape and is divided into two sealed compartments: a wet chamber and a dry chamber. The system is equipped with wastewater filtration devices, and the internal pump components include heating elements. This type of equipment is recommended for use in low-temperature regions.
Reliable operation of a sewage pumping station depends on the correct selection of equipment. Therefore, before purchasing and installing an SPS, it is necessary to carefully evaluate equipment specifications, site conditions, and the requirements of technological processes.
Standard configuration of a sewage pumping station includes:
- a durable housing with stiffening ribs made of stainless steel, fiberglass, plastic, or other corrosion-resistant materials;
- pumps for wastewater transfer;
- pressure pipelines;
- shut-off and auxiliary valves regulating liquid inflow;
- automation systems for operation control and liquid level monitoring.
Operating Principle of a Sewage Pumping Station
Wastewater flows through pipelines into the receiving tank of the sewage pumping station, where the pumps are installed. The pumps transfer the wastewater into a pressure pipeline, from which the medium is discharged into the sewer system.
The distribution chamber is equipped with gate valves and a check valve. The gate valves control the discharge of liquid into the pipeline. During normal operation, the valves remain open, while during maintenance or repair they are closed. The check valve prevents wastewater from flowing back into the system.
Advantages of Sewage Pumping Stations
The main advantage of sewage pumping stations is their ability to efficiently remove wastewater when gravity-based transportation to treatment facilities is not possible. Additional advantages include:
- use of high-quality polymer materials resistant to aggressive substances, ensuring reliable operation and long service life;
- complete configuration with equipment required for liquid transfer, including automation systems, shut-off valves, safety valves, and drainage pumps;
- compact design — a sewage pumping station occupies significantly less space than reinforced concrete wastewater storage tanks, allowing optimization of drainage system layouts;
- cost efficiency — automated control systems activate pumping equipment only when the tank reaches a preset filling level, reducing electricity consumption.
How to Choose a Sewage Pumping Station
First of all, sewage pumping stations differ in pump characteristics, including operating principle, design features, capacity, and power. Other important selection criteria include:
- composition of wastewater;
- location of the inlet collector;
- required pumping head and distance to the discharge point;
- volume of wastewater entering the system;
- project-specific requirements;
- terrain characteristics;
- type of pumping equipment and control method.
To select and purchase the most efficient sewage pumping station, an individual engineering calculation is required. This calculation should take into account the required configuration, dimensions, maximum and operating capacity of the unit.
Only specialists with appropriate qualifications and technical expertise can ensure compliance with all engineering and construction standards during installation. Therefore, for stable and uninterrupted operation, sewage pumping stations should be designed and installed by professionals.
More detailed information on configurations, technical characteristics, and pricing of the sewage pumping stations we offer is available by phone using the number provided in the “Contacts” section. ZIKO managers also provide consultations and accept equipment supply requests via email or through the feedback form on our website.
- Published in Промислові насоси для води – рішення, Рішення
Industrial Grease Traps for Enterprises
Інжинірингова компанія «ЗІКО» пропонує якісні і недорогі побутові та промислові The engineering company ZIKO offers high-quality and cost-effective domestic and industrial grease traps for enterprises across various industries. The company designs, develops, and configures water treatment systems in accordance with the specific requirements of customers’ technological processes. ZIKO also supplies high-quality water filters, reverse osmosis membranes, and ready-made solutions for water treatment and water preparation with delivery throughout Lviv and across Ukraine.
Purpose of Industrial Grease Traps
A properly selected industrial grease trap ensures effective treatment of domestic and utility wastewater discharged into sewer systems. The separation unit removes synthetic, animal, and vegetable fats from the effluent.
Areas of Application
Industrial grease traps for sewer systems are used in various industries involved in the production of:
- pharmaceutical products;
- cosmetic products;
- canned goods;
- vegetable oils;
- meat and dairy products;
- soap, adhesives, and other goods.
Industrial grease traps are also installed in hotels and food service facilities, including restaurants, bars, and cafés.
Advantages of Industrial Grease Traps
The key advantages of industrial grease traps for restaurants and production facilities include:
- High water treatment efficiency. The presence of multiple chambers with baffles ensures effective separation of fats. Only treated water free of grease particles enters the sewer system, preventing pipe corrosion and clogging.
- Flexible selection of dimensions and capacity according to technological requirements and water consumption volumes.
- High strength, low weight, and long service life.
- Internal baffles and flow dampers that prevent grease from entering the sewer system.
- Corrosion-resistant materials used in manufacturing.
- Affordable equipment cost and ease of installation.
- Reliable and silent operation.
- Energy efficiency. Grease traps operate without electricity.
- Simple and low-cost maintenance. Industrial grease traps require only regular cleaning and washing.
Types and Materials of Industrial Grease Traps
Grease separators are classified according to their installation method and materials of manufacture. For industrial applications, three main types are available:
- Above-ground units — installed in dedicated indoor spaces.
- Underground units — buried in the ground in designated locations.
- Under-sink units.
The most commonly used materials for manufacturing industrial grease traps include:
- Stainless steel. High-cost but extremely reliable and durable units.
- Fiberglass. Resistant to aggressive chemical agents and suitable for facilities where chemically aggressive cleaning products are used.
- Plastic. Polypropylene grease traps are widely used in hotels, restaurants, cafés, and bars. Their service life can reach up to 30 years; they are easy to maintain and environmentally safe.
Industrial Grease Traps for Hotels, Restaurants, and Cafés

Installation of a grease trap in a hotel or restaurant ensures effective treatment of wastewater from sinks. This prevents environmental contamination and guarantees reliable operation of sewer systems.
Installation Options for Grease Separators
There are several installation options for grease separators used in restaurants and cafés:
- Under-sink installation — easy to service, clean, and wash.
- Installation in a utility room. As a rule, high-capacity grease traps for restaurants or hotels are installed in specially designated service areas.
- Underground installation. Such grease traps are buried in designated outdoor areas. The equipment is selected based on the facility’s operational specifics and wastewater volume.
Selection of an Industrial Grease Separator
Before purchasing a grease trap, it is necessary to select a model that best matches the requirements of the enterprise or facility. Key factors include production output or number of prepared meals, maximum wastewater volume, and the concentration of grease contaminants.
Our specialists can assist in calculating the required capacity of a grease trap for a restaurant or café kitchen.
If domestic wastewater contains only grease particles, stainless steel or plastic grease traps are suitable. For wastewater containing chemically aggressive substances, fiberglass grease separators are recommended.
For a more detailed consultation on selecting an industrial grease trap for sewer systems, please call the phone number provided in the “Contacts” section. Company managers will help select the most effective equipment and provide information on pricing, delivery terms, and lead times.
Product supply requests are also accepted via the website feedback form and the company’s email address.

Інженер-технолог відділу екологічної інженерії на об’єкті
- Published in Промислові системи очищення стоків – рішення, Рішення
Domestic Grease Traps for Sewer Systems
ZIKO supplies domestic and industrial grease traps for sewer systems of various types. The company’s specialists design, develop, and install turnkey water treatment solutions. ZIKO also offers, at competitive prices, a wide range of water filters, reverse osmosis membranes, systems, and equipment for effective treatment of wastewater and drinking water.
Purpose of a Domestic Grease Trap
A compact under-sink grease trap removes oily and greasy impurities from water used for dishwashing and other household needs. This reduces the negative impact of fats on metal sewer pipes and helps prevent pipeline blockages. A domestic grease trap converts household wastewater into technically treated water that is safe for both the environment and sewer systems.
Advantages of an Under-Sink Kitchen Grease Separator
In addition to affordability, domestic kitchen grease traps offer several advantages:
- wastewater purified from grease particles does not clog sewer systems;
- high-quality manufacturing materials provide corrosion resistance;
- sealed lids prevent the spread of unpleasant odors;
- simple design allows for easy and low-cost installation and connection.
Grease Trap Design
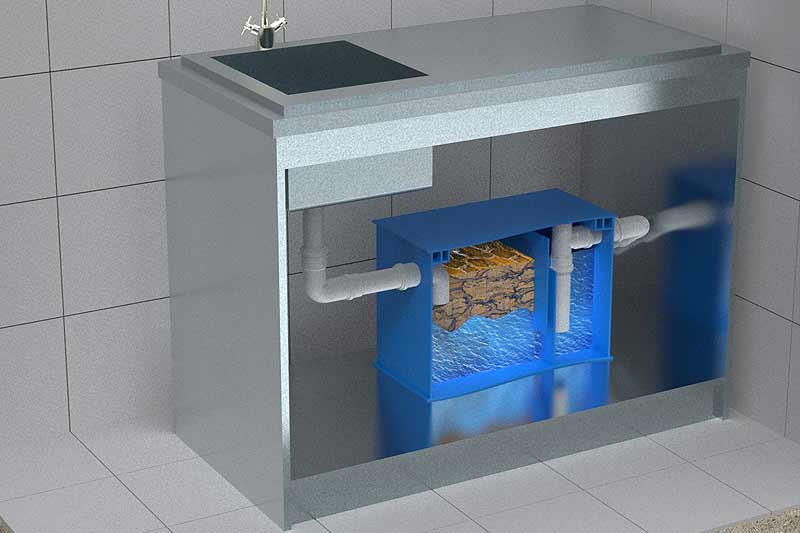

A domestic kitchen grease trap consists of the following structural components:
- a housing made of corrosion-resistant material with inlet and outlet connections;
- one, two, or three internal baffles that divide the grease trap into several chambers and slow down the water flow;
- a sealed lid with a rubber gasket, which prevents the spread of unpleasant odors resulting from the decomposition of grease particles inside the separator.
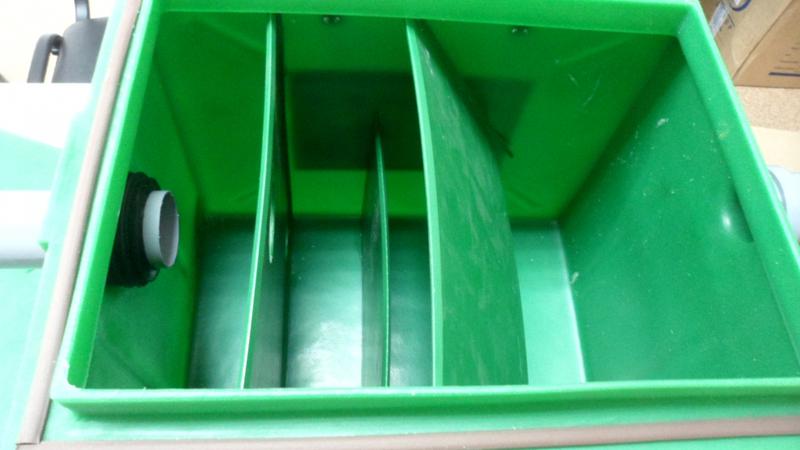

Operating Principle of Grease Traps
Domestic grease traps for sewer systems operate according to the following principle:
- Contaminated water from the sink enters the first chamber of the separator through the inlet connection. During sedimentation, grease impurities separate from the water and float to the surface.
- At the next stage, grease particles accumulated in the first chamber settle at the bottom of a dedicated tray, where they are retained.
- The water then flows through a lower connection into the second chamber of the separator, where final separation of grease residues not removed in the first chamber takes place.
- At the final stage, the treated water is discharged from the grease trap through the outlet connection into the sewer system.
During wastewater treatment, undissolved particles accumulate in the first chamber of the domestic grease trap; therefore, the separator requires regular cleaning and washing.
Classification and Materials of Grease Traps
All domestic grease traps for sewer systems operate on the same principle. However, models may differ in installation method. Some grease traps are installed horizontally, while others are designed for vertical installation. The choice depends on the layout and direction of the sewer pipelines.
Under-sink domestic grease traps are manufactured from corrosion-resistant materials, including:
- Metal. Grease traps made of stainless steel or aluminum are efficient and durable but relatively expensive. Metal separators are highly reliable, long-lasting, and easy to clean.
- Fiberglass. Fiberglass under-sink grease traps are strong and resistant to chemical exposure. Such units can be installed outdoors or buried underground.
- Polyethylene and polypropylene. Grease traps made from these materials are affordable, lightweight, and easy to maintain.
Criteria for Selecting Grease Traps for Sewer Systems
Before selecting and purchasing a grease trap, it is necessary to determine a number of key parameters the unit must meet:
- Available space under the sink. Clearance must be provided above and on the sides of the separator for pipe connection and lid removal.
- Number of sinks. When calculating grease trap capacity, the total wastewater volume from all active taps must be taken into account.
- Diameter of sewer pipes and inlet/outlet connections. These must match to allow installation without special adapters.
- Wastewater composition. If the effluent contains a high concentration of solid particles, a grease trap with multiple internal baffles is recommended.
- Sink volume. In some cases, rapid discharge of a fully filled sink is required. The grease trap documentation must specify the maximum volume of water that can be supplied to the unit at one time.
- Material of manufacture. If the separator is installed in a visible location, a stainless steel grease trap is preferable. For under-sink installation, a cost-effective plastic model is usually sufficient.
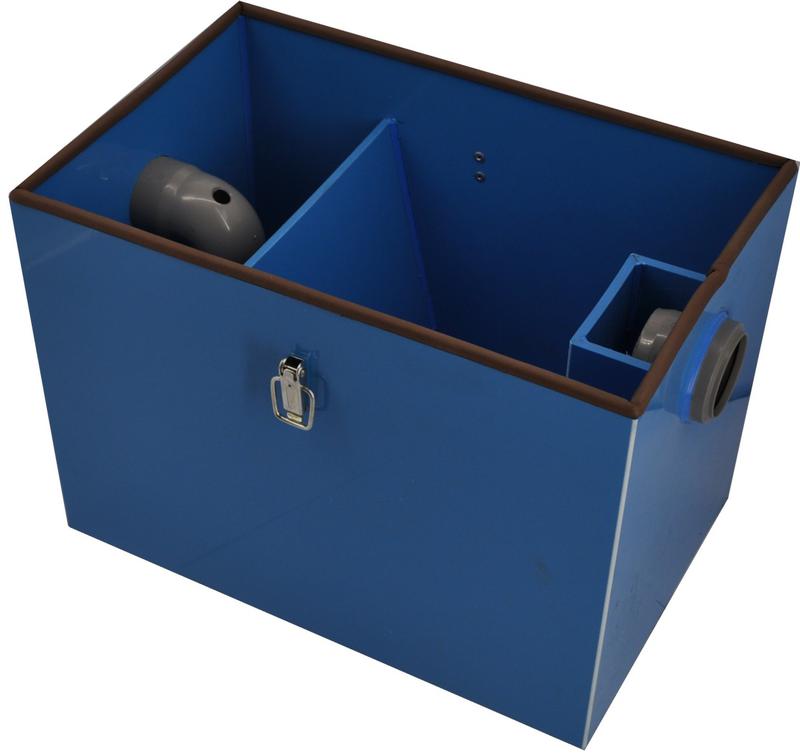

You can purchase a domestic under-sink grease trap for a kitchen sink from the ZIKO online store. By calling the phone number provided in the “Contacts” section, you can obtain comprehensive information on pricing, technical characteristics, and delivery terms.
Product supply requests are also accepted via email and through the feedback form on the company’s website.
- Published in Побутові системи очищення стоків – рішення, Рішення
Types and Categories of Surface Industrial Pumps
Various models of industrial surface pumps are designed for pumping large volumes of water or liquids with specific properties. These pumps are installed above the liquid surface and are classified into several types:
- automatic;
- self-priming;
- pumping stations.
Automatic Industrial Surface Pumps
For optimal operation of equipment and systems, automatic surface pumps are equipped with protective automation. This automation may be integrated into the pump or supplied as a separate system. In addition to optimizing operation, such control systems protect pumps from:
- voltage fluctuations in the power supply;
- operation at critically low liquid levels in tanks or water sources;
- excessive temperature of the working medium in water supply and water treatment systems.
Self-Priming Industrial Surface Pumps
There are two types of self-priming industrial surface pumps:
- Ejector-type — suction of the working medium is ensured by the pump design itself.
- Non-ejector-type — liquid intake occurs due to vacuum created inside the pump chambers.
Such industrial surface pumps are used:
- in agriculture, including irrigation systems;
- for domestic and industrial applications;
- in water treatment and wastewater systems;
- for pumping drinking water;
- for water intake from natural and artificial reservoirs.
Industrial Surface Pumping Stations
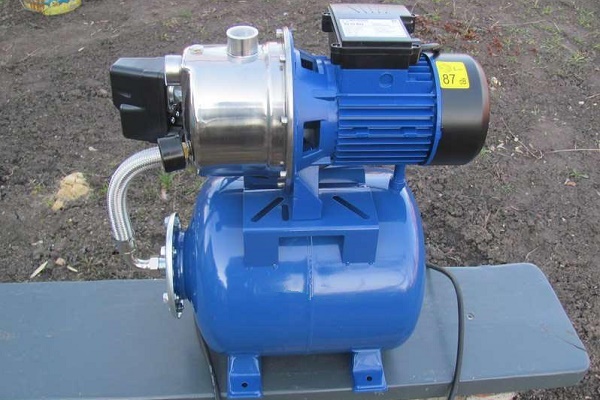

Industrial surface pumping stations operating in automatic mode are designed for pumping liquids from tanks and reservoirs, as well as for water intake from wells or open water bodies. Automation responds to system pressure by regulating pump operation (switching it on and off), thereby ensuring stable and constant pressure in the system.
Advantages of Industrial Surface Pumps
Industrial surface pumps offer the following advantages:
- no need to seal electric motors;
- simple and cost-effective maintenance and repair, with the possibility of system upgrades;
- convenient access to all components;
- low weight and compact dimensions;
- high reliability and long service life;
- affordable cost.
ZIKO supplies a wide range of industrial surface pumps and automatic pumping stations at competitive prices, with delivery throughout Ukraine. The company also provides reliable equipment for water treatment, as well as industrial and domestic wastewater treatment.
By calling the phone number listed in the “Contacts” section, you can consult with company managers regarding pricing, quality, intended application, and product availability. Equipment supply requests and cooperation proposals are also accepted via the website feedback form or by email.
- Published in Промислові насоси для води – рішення, Рішення